Kamagra Polo
"Buy 100mg kamagra polo amex, erectile dysfunction help".
E. Jaroll, M.S., Ph.D.
Program Director, Stanford University School of Medicine
This pin ought to interact the primary metatarsal erectile dysfunction medicine in homeopathy discount kamagra polo 100 mg visa, the first cuneiform bone erectile dysfunction treatment home remedies buy kamagra polo with mastercard, the navicular erectile dysfunction drugs herbal buy 100mg kamagra polo visa, and the talus impotence caused by medications buy kamagra polo mastercard. The lateral pin is started distal to the flare at the base of the fifth metatarsal and is aimed medially and slightly dorsally, crossing the cuboid bone and coming into the calcaneus. The patient is then ambulated with a three-point, nonηeight-bearing crutch gait for 6 weeks. A short-leg strolling cast is applied, and the patient is permitted partial weight bearing for an extra 4 to 6 weeks, at which time healing should be full. B Removal of a dorsally based mostly wedge from the tarsal bones to right a hard and fast cavus deformity with its apex within the midfoot has been described by Cole (63). This disadvantage is offset by preservation of the metatarsalδarsal joints distally and the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints proximally. Because this operation corrects only the cavus deformity, the absence of fixed-heel varus is a prerequisite. Jhass (66) has described an analogous osteotomy that removes the wedge distally, excising the metatarsalδarsal joints. The talocalcaneal, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints are resected, separating the foot into three movable segments: the forefoot, the calcaneus, and the talus and ankle mortise. If the correct wedges of bone are resected, the position of the foot will be correct when the bony surfaces are apposed. More importantly, it has been shown in plenty of long-term follow-up studies that triple arthrodesis causes stress shifting and premature degenerative arthrosis (19Ͳ1, 26, 27, 55) or Charcot arthropathy (82) in adjoining unfused joints, such because the ankle joint. Furthermore, Schwend and Drennan (72) have shown that, even after solid triple arthrodesis, there could be progressive deterioration and recurrence of deformity over time secondary to muscle imbalance. Before starting the triple arthrodesis operation, the surgeon should give some thought and planning relating to the wedges of bone to be eliminated and, specifically, the amount of bone to be eliminated. Simplify the cuts to parallel and perpendicular in relationship to apparent large bony landmarks. Visualizing the foot at surgical procedure and making the osteotomy cuts to create the wedges, as described in the subsequent discussion, appears much more practical and accurate. The commonest deformity for which triple arthrodesis is performed is fastened cavovarus deformity. To right this deformity, a laterally based wedge of bone is faraway from each of the joints to be resected. The wedge that can allow correction of the forefoot will excise the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints. To achieve correction to a neutral position, the distal cut is perpendicular to the long axis of the forefoot and the proximal reduce is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the calcaneus (A). To right the varus of the hindfoot, a laterally based wedge should be faraway from the subtalar joint. To appropriate the heel to a neutral place, the proximal cut from the undersurface of the talus should be perpendicular to the lengthy axis of the tibia (or parallel with the ankle mortise), whereas the distal cut from the superior surface of the calcaneus ought to be parallel to the bottom of the heel (B). This is as a end result of the medially based wedges which are created utilizing the espoused principles must be removed from the lateral facet (C). This task is simplified if all the joints are broadly released by intensive capsulotomies and the interosseous ligament of the subtalar joint is sectioned. In this circumstance a posteriorly primarily based wedge is faraway from the subtalar joint, which permits correction of the calcaneus deformity. A dorsal wedge is removed from the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints to enable the forefoot to be dorsiflexed (D). The triple arthrodesis operation is illustrated for the most typical deformity: cavovarus. The affected person is placed on the operating desk with a sandbag underneath the hip on the aspect to be operated, thus bringing the lateral aspect of the foot into higher position.
Additional cancellous bone graft is added over this graft and held in place by the periosteum and muscles when the wound is closed erectile dysfunction can cause pregnancy cheap 100 mg kamagra polo visa. Decision making is considerably troublesome and controversial within the case of the asymptomatic mature affected person with hip dysplasia erectile dysfunction treatment in kerala discount 100 mg kamagra polo free shipping. For the asymptomatic adolescent with minimal radiographic dysplasia (because degenerative arthritis is a likelihood but not a certainty) impotence reasons kamagra polo 100 mg low cost, the creator prefers to inform the family about the potential for an opposed pure historical past and recommend surgery only at the onset of symptoms erectile dysfunction beta blockers generic 100 mg kamagra polo with visa. There is usually a long interval between the onset of symptoms and degenerative joint illness as evidenced on radiographic photographs (67). The patient can be reassured that if symptoms develop, surgical therapy can help in avoiding long-term degenerative joint illness. However, confronted with an adolescent with radiographic evidence of subluxation, regardless of the signs, the creator recommends surgical correction, because without therapy an adverse pure historical past is definite. Over the last a quantity of years, as more has been learned about the pure history of hip dysplasia (26, 67, 171, 213, 216, 221, 222, 225, 378, 460, 509͵11), much consideration has been focused also on acetabular rim syndrome (overload of the acetabular rim) (224) in younger adults as a major illness, or as a residual of childhood hip illness. They could describe symptoms corresponding to sudden "locking" or a clicking sensation (454). These sensations are precipitated by movements that mix hip flexion, adduction, and inner rotation. As the site of acetabular rim overload is normally anterior, signs are provoked on physical examination by the so-called impingement check. Films taken in a weight-bearing situation and false profile lateral views will present proof of dysplasia, as beforehand discussed. One may also see proof of an acetabular rim fracture suggestive of the rim overload (224, 454). During the exposure, the mirrored head of the rectus tendon must be identified, dissected free from the capsule, and divided someplace between its midportion and its junction to the conjoined tendon. The surgeon should decide whether or not that is the true or false acetabulum, based on which of the two affords the higher stability and congruity. The acetabulum is recognized by creating a small incision in the capsule or by inserting a probe. The right location should be verified radiographically by placing a information pin into the ilium at the presumed acetabular edge. In some instances, it could be necessary to skinny the capsule to allow the graft to be placed in the correct location. After the right location is verified, a 5/32-inch drill is used to make a sequence of holes at the fringe of the acetabulum. These holes must be drilled to a depth of about 1 cm and may incline about 20 degrees, as illustrated. They should extend far sufficient anteriorly and posteriorly to provide the mandatory protection. Alternatively, a high-speed burr can be utilized to initiate the groove which can be then deepened and angled with straight and angled curettes. If a drill is used to make holes, a slender rongeur is used to join these holes and produce the slot. The floor of this slot ought to be the subchondral bone of the acetabulum, and it must be degree with the capsule.

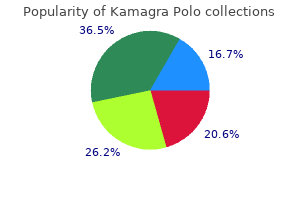
The most generally used method of assessing skeletal maturity is utilizing the bone age impotence journal buy kamagra polo 100 mg cheap, as described by Greulich and Pyle (87) erectile dysfunction hernia buy kamagra polo us. The orthoradiograph technique exposes every joint individually impotence and alcohol discount kamagra polo 100 mg without prescription, thereby making certain that the x-ray beam through every joint is perpendicular to the x-ray movie and thereby avoiding errors of magnification erectile dysfunction caused by nervousness best order for kamagra polo. As the ossification centers seem and coalesce in a reasonably predictable fashion, they had been capable of develop a norm for every age. While helpful, it does have important deficiencies including gaps as far as 14 months, thus giving a rather massive standard error. While the average or imply radiograph would probably be chosen for a given skeletal age (placing half the youngsters as extra mature and half the youngsters as less mature), the builders chose a number of the standards based on what they subjectively felt were most representative of that age. Furthermore, whereas a general order of ossification occurs in the bones of the hand and wrist, variations do occur; subsequently arbitrary selections in age must be made. The applicability of these "requirements" to different ethnicities and to modern-day children has been questioned. Recent studies have shown youngsters to achieve an older bone age for a given chronological age at present versus 25 years in the past (88). Similarly, bone ages of Asian and Hispanic kids are inclined to be overestimated utilizing the Greulich and Pyle technique. They seem to mature ahead of the Caucasian and African American kids (89). Recent advances have used computer-based methods to rating the x-rays and determine the skeletal age (902). One of these methods has concerned the recent acquisition of an atlas of 1,four hundred kids from 4 different ethnicities to attempt to restrict any ethnic bias from the standards (89). The Tanner-Whitehouse atlas provides requirements for 20 different landmarks of the hand and wrist and permits determination of the skeletal age. The radiograph is in comparison with standard radiographs, and each of the 20 landmarks is designated a letter rating. A numeric rating is derived from this letter score after gender is taken into account. Dimeglio (94) has shown accuracy in using a modification of the Sauvegrain technique of bone age particularly within the prepubertal and pubertal youngsters. This French method appears at the four completely different ossification centers in regards to the elbow and develops a most 27-point score for women and men. The score is then plotted on a graph and the suitable bone age (at 6-month intervals) may be decided. This methodology has been proven to be very reproducible and is good for kids on this age group. For instance, one would expect a 3-cm discrepancy from a femur shaft malunion in a 12-year-old boy to stay stable as the expansion plate is unaffected and the affected person is unlikely to recoup the gap with regrowth. In distinction, a Salter Harris sort I distal femur fracture with complete growth arrest will continue to worsen till skeletal maturity. In congenital limb variations, the ratio of the quick limb to the long limb has been proven to be constant (97). Clinically, these limbs will stay proportionately the same, but the absolute difference in size will improve (98). Some generalities may be made about the existing congenital deformity in accordance with the patient age.

Macrodactyly could also be static erectile dysfunction reasons generic kamagra polo 100 mg on line, in which the digit is enlarged at birth and development is proportional to the normal digits impotence versus erectile dysfunction buy kamagra polo no prescription. Alternatively zopiclone impotence buy kamagra polo 100 mg with mastercard, it might be progressive erectile dysfunction qof generic 100mg kamagra polo overnight delivery, in which case the involved digit grows disproportionately sooner than the traditional ones (429). Although the appearance is often grotesque, the main disability is with shoe fitting. A: Macrodactyly most commonly entails the second ray; in this case, the hallux and third toe are concerned to some extent. B: Radiographic look demonstrates enlargement of bone as well as gentle tissue. C: Clinical look after second ray resection and third toe interphalangeal joint disarticulation. Surgical options embody soft-tissue debulking, ostectomy, epiphysiodesis, full or partial toe amputation, and ray resection, either as isolated procedures or in combination (425, 426, 430ʹ33). A mixture of soft-tissue debulking with epiphysiodesis of the proximal phalanx or metatarsal or each is really helpful for delicate, static deformities. Large residual circumference of the foot, somewhat than length, is usually the greater problem for shoe fitting. Adduction of the metatarsals creates a concave medial border of the foot, a convex lateral border, and prominence on the base of the fifth metatarsal. Bleck (444, 445) published two classification methods: one based mostly on the severity and one on the flexibleness of the deformity. Berg (446) developed a classification system for metatarsus adductus and skewfoot primarily based on radiographs of the feet of a small group of youngsters between the ages of two and 17 months. Radiographs are indicated for the older youngster and adolescent with severe residual deformity, ache, or different incapacity when operative intervention is being thought-about. Ruth Wynn-Davies reported the incidence of metatarsus varus at 1 in 1000 live births and 1 in 20 in siblings of patients with metatarsus varus (94). The actual incidence is unknown due to the shortage of a strict definition of the condition. An elevated reported incidence during the past century is probably because of an elevated awareness of the situation by major care physicians (5, 436ʹ38). Although earlier studies (439, 440) indicated an affiliation of metatarsus adductus with hip dysplasia, more modern research (441, 442) have shown no vital association between the 2 conditions. The severity of metatarsus adductus is set by the relation between the toes and the distal finish of the line bisecting the heel. B: A flexible foot could be passively overcorrected into abduction with little effort. Whereas some authors have proposed the etiology to be joint malalignment deformity secondary to in utero positioning, others have proposed the etiology to be muscle imbalance ensuing from contracture and anomalous insertion of the tibialis anterior (437, 448, 449) or tibialis posterior (450). Two research on cadavers with metatarsus adductus have documented an abnormality in the shape of the medial cuneiform (451, 452). No patient required surgical correction and hallux valgus was not an recognized downside. The percentage of feet with metatarsus adductus that bear spontaneous correction without treatment may actually be even greater than reported in these studies, because of the chance of underreporting of delicate, flexible circumstances. Rushforth prospectively studied the natural historical past of metatarsus adductus in 83 children with 130 affected toes who obtained no treatment (6). Eighty-six p.c were normal, 10% were reasonably deformed and asymptomatic, and 4% have been deformed and stiff at a median followup of seven years.

